Conditionals let you make decisions in your code.
if else
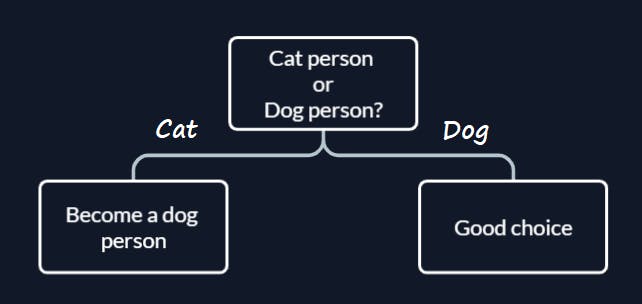
choice = input("Cat or Dog?")
if choice == 'dog':
print("Good choice")
else:
print("Become a dog person")
Nested if else
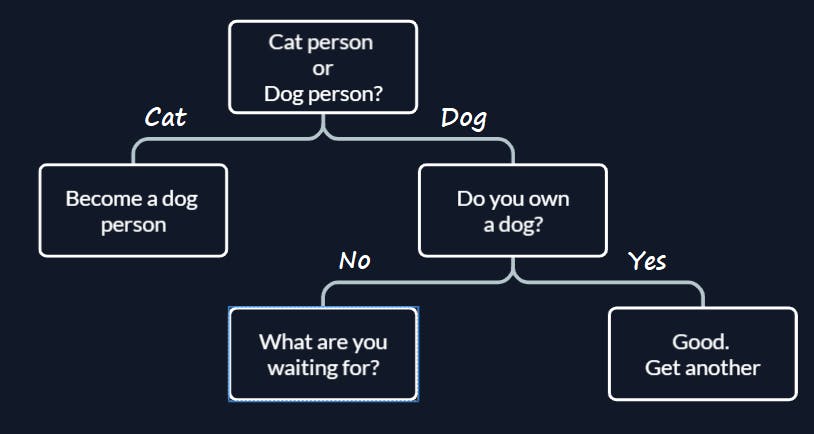
choice = input("Cat or Dog?")
if choice == 'dog':
print("Good choice")
owner = input("Do you own a dog?")
if owner == 'yes':
print("Good. Get another")
else:
print("What are you waiting for?")
else:
print("Become a dog person")
if elif else
If you have more than one condition to check against use elif.
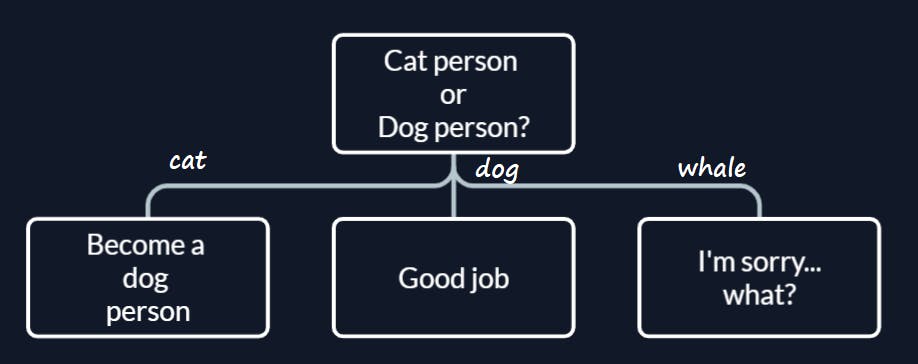
choice = input("Cat or Dog?")
if choice == 'cat'
print("Become a dog person")
elif choice == 'dog':
print("Good choice")
else:
print("I'm sorry... what?")
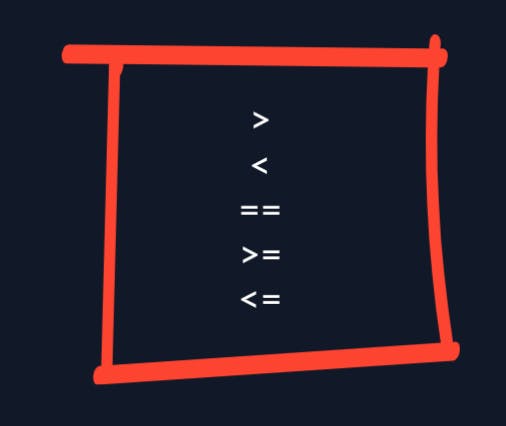
Comparison operators
In our conditionals, comparison operators help us to compare more than one value, or have more than one condition.
Modulo
The modulo operator % return the remainder of a division. So basically
10 = 3+3+3+1
10%3 = 1
However in programming I have learnt over time and a lot of digging that this operator is a bit more powerful than it seems to be. Basically the operator can help you set upper bounds.
Example: x%5
For any value of 'x' our result will be a number from this given list [1, 2, 3, 4]
Logical operators
To help combine multiple conditions

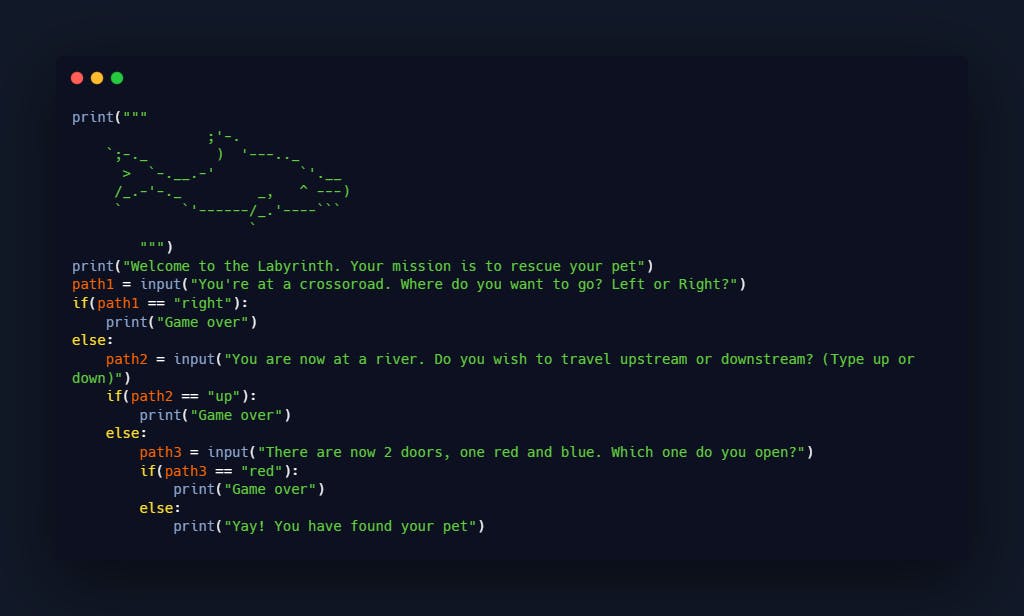
Project - Rescue your pet